Debbie Landa, Clare Ryan and the Dealmaker Media team are part of the reason that I love GROWConf and GROWtalks. They put on amazing events by putting entrepreneurs first, foremost, and front and centre. They are bringing GROWtalks to Toronto (Feb 21) and Montreal (Feb 19). And we have a discount code at the end of the post.
“A hands-on playbook for creating startup success”
I like learning by example. It’s a mixture of seeing what worked for someone else, and then trying the appropriate tactics customized for my situation. The challenge is trying to do with more efficiently than 9 or 10 coffee meetings. GROWtalks brings together the best entrepreneurs, who are killing it, and has them present what is working for them. THis is what GROWtalks is, an event for entrepreneurs with entrepreneurs sharing their strategy, tactics, metrics and successes, even the failures. (Full disclosure: I am MCing the GROWtalks event, however, I am not being compensated for this, but I do get the opportunity to participate and learn).
Check out photos from the 2012 GROWtalks event in Vancouver:
It’s rare we get this many awesome startup founders all talking about the hard part of their business. I know that all of these folks will be around throughout the day, they’ll be hanging out, answering questions. It’s going to be a fantastic day. Check out the line up:
- Brant Cooper LinkedIn Follow @brantcooper
- Mike Beltzner LinkedIn Follow @beltzner
- Kate Rutter LinkedIn Follow @katerutter
- Laura Fitton LinkedIn Follow @pistachio
- Danielle Morrill LinkedIn Follow @daniellemorrill
- Scott Kveton LinkedIn Follow @kveton
- Dan Martell LinkedIn Follow @danmartell
- Michael Litt LinkedIn Follow @michaellitt
- Mark Organ LinkedIn Follow @markorgan
I might be biased. My employer is an investor in some of the presenters. My cofounder is one of the presenters. But I’m honestly stoked about the speakers. I’m really looking forward to hearing Beltzner, Rutter, Fitton and Morrill. The mix of product, early customer acquisition and understanding lifetime value are converations I have with almost every founder. I’m very curious to hear the opinons, experiences and thoughts of this group.
Part of my MCing was to request StartupNorth logo tattoos for all the speakers (we’ll see if that happens), and a discount code. Register before Februrary 1, 2013 and get 10% off (use promotional code: startupnorth). It reduces the ticket price from $195 to $175.50.
GROWtalks Toronto
February 21, 2013, 10am-4pm
Size: 200-300 people
Speakers: 9 Industry leaders
Time: 10am-4pm
Website: www.growtalks.com
Toronto: http://www.growtalks.
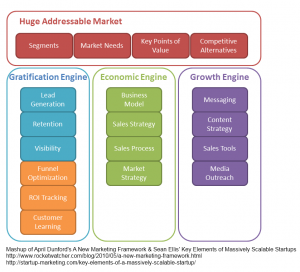
GROWtalks is a one day conference focused on how to create simple, actionable metrics, and use them to make better product and marketing decisions for startup success. Industry experts will share actionable advice to startup teams on how to improve design, product and customer development, acquisition, retention, and more.
Topics Covered:
- Customer Development
- UX/UI Design
- Growth Hacking
- Customer Retention
- Fundraising
- Customer Engagement
- Product Development