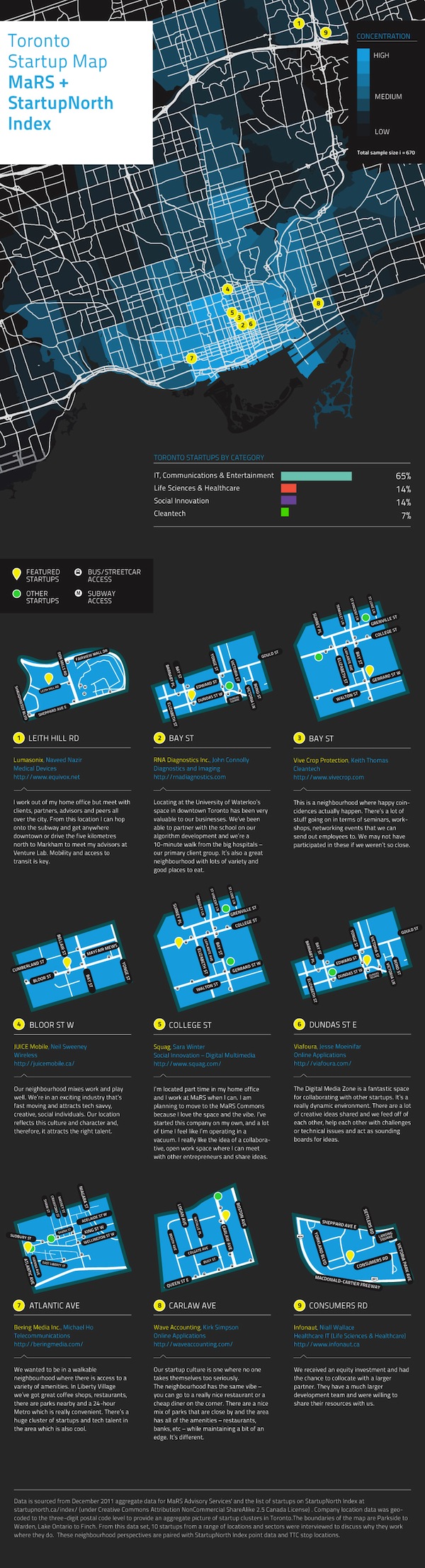
Joe Greenwood is directing a new project that pulls together data to track Ontario’s startups. One of the first data sources to be tapped was the StartupNorth Index, which in conjunction with MaRS client data has been crunched into a heatmap of 670 startups across Toronto. Not surprisingly, the ideal office is inexpensive, accessible by transit, and close to good coffee. How can you help fill in this map? Build an amazing startup of course.
-
If you want to change the ecosystem you need to build an amazing startup
At Founders and Funders this week we took some time to interview Dan Debow. It was a bit of a love-in I admit but that is just because I really love how much passion Dan has for helping those around him. He has made a big difference in a lot of people’s lives. I’ve benefitted from it and so have dozens of others in the Canadian startup community.
One thing that Dan said really struck me. A little context might help though.
A lot of folks have been working hard to build a startup ecosystem in Toronto. For over half a decade guys like Dan have been pouring energy in to helping anyone with an idea and a glimmer in their eye to start a startup. There are of course formal organizations that do this on behalf of the government, but the fact is that making Toronto a viable city for startups has been a mostly clandestine movement. People working on the fringes to do what they believe in.
Sometimes you hear complaints about the ecosystem. Whether it is Toronto, Montreal, Calgary, Edmonton, Vancouver or Halifax you can find complainers.
“How can we fix the local ecosystem?”
Dan said it best this week and he was clearly passionate about it: You can’t fix your ecosystem. Just get out there and build something great. More accurately he said:
That’s your job. Your only job. Get out there and build something great.
You can stop being shy, coy and tepid about it. Everyone around you wants you to do something great. They just want you to step up a little and say you are going to do it.
I want you to do something great. I want you to put a ding in the fucking universe.
Take your vision and make it even hairier, bolder and broader. Take your product and get obsessed with it. Change the world for people around you and every single one of us will step in line and push behind you.
Dan did it and this week we got to shine the spotlight on him a bit. There are hundreds of folks out there pushing to do it. Stop worrying about the community. Go big and the community will be right there behind you.
The next time we plan a Founders and Funders I want it to be you that’s up there telling your story.
You can be next. JFDI
-
Ctrl Alt Compete – A startup documentary
Interesting my friends from Microsoft are hosting a screening of Ctrl Alt Compete which features our own Josh Sookman (LinkedIn, @jsookman) of Guardly and Brian Wong (LinkedIn, @brian_wong) of Kiip. It’s a documentary about building startups and the founders passion, fortitude and the shear insanity of doing this. Looks like a fun take, realistic take.
- Toronto – March 6th 8:30am – 12pm Register »
- Montreal – March 13th 8:30am -12pm Register »
Watch the trailer.
The movies takes a revealing look at the startup and emerging business scene through the eyes of five founders and their teams telling a story of the passion, fortitude and insanity that is bringing a startup to life. Microsoft believes tech entrepreneurship is fundamentally changing the world. The things that developers create; the ideas that they’re able to make reality; the tangible value they deliver is reshaping the way people live their lives every day. Building a startup from nothing to something is hard—REALLY hard.
Red Carpet Event for the Canadian Premiere of Ctrl Alt Compete Screening
Join a networking crowd of investors, community start-ups and entrepreneurial students for the first Canadian screening of Ctrl Alt Compete – a Microsoft movie documentary on what it takes to be a start-up:Passion. Fortitude. Insanity.
There are lots of tech startups out there taking their shot at changing the world. There’s no shortage of ideas. The infrastructure to build quickly is cheaper and more accessible than it’s ever been…there’s lots of capital floating around for the right idea. If only it were that simple! Building a startup from nothing to something is hard—REALLY hard. There is a “story behind the story” of just how hard it is to go from inception to reality and become the products and services that we use every day.
It’s a story of the power of people pouring their passion, drive and dedication into building something that changes the world—no matter how hard.
We believe that is a story worth telling and sharing.
At this premier screening event, you’ll hear insights from industry executives, Start-Ups from the cast and local leaders in the Start-Up community.
-
2011: Glass Half-Full or Half-Empty for Canadian VC?
Editor’s note: This is a cross post from Mark Evans Tech written by Mark Evans of ME Consulting. Follow him on Twitter @markevans or MarkEvansTech.com. This post was originally published in February 14, 2012 on MarkEvansTech.com.

 Some rights reserved by waferboard
Some rights reserved by waferboardFirst, the good news about Canada’s venture capital landscape. In 2011, investment activity climbed to the highest level in four years ($1.5-billion), a 34% increase from 2010, although it is still significantly below the record activity ($2.1-billion) reached in 2007.
The bad news is there’s still not enough supply to meet rising demand, plagued by “continued weakness” when it comes to fund-raising.
The good news-bad news scenario was spelled out in the Canadian Venture Capital Association’s annual report. For those of us in the glass half-full camp, the increase in investment and the number of deal is cause for optimism.
As well, 2011 saw a spike in M&A activity with 34 deals, including two each by Google, Facebook, Zynga and Salesforce.com. And there was a flurry of incubators and accelerators established, including Extreme Startups last week.
Before anyone gets carried away, Canada’s venture capital landscape is a long, long way from being solid, let alone robust. There’s still not enough venture capital for seed, series A or major rounds. And don’t expect U.S. investors to pick up the slack.
In a press release, CVCA president Gregory Smith said there is concern about whether enough fund-raising can be dong to support the demand for investments. This situation was illustrated by the fact new commitments to Canadian VCs were flat last year at $1-billion.
“Canada has a historic opportunity to become an innovation leader,” Smith said, adding that “in order to act decisively on this opportunity, we must first overcome challenges to supplying VC funds that, in turn, supply entrepreneurs.”
So what’s the solution? How can Canada’s venture capital community do a better job of supporting the startup community? There is not easy answer to a problem that has been around a long time and doesn’t look to be changing any time soon. It’s not going to be an easy fix from government or U.S. investors or institutional investors waking up to the idea of venture capital investing.
Perhaps the answer to the problem is this: success. If more startups and mature high-tech companies are acquired, that could (emphasis on “could”) encourage investors (angels, VCs and institutional) to get more involved. Success has a strange way of helping people to see the light or new opportunities that they otherwise would have dismissed or not seriously considered.
That said, success is a double-edged sword. Without enough financial support, it is hard for startups to have enough powder to become acquisition targets. If they’re not interesting targets, there’s no acquisitions and, likely, less interest from investors.
So which side of the fence do you sit on? Are you bull or a bear about Canada’s VC landscape?
Editor’s note: This is a cross post from Mark Evans Tech written by Mark Evans of ME Consulting. Follow him on Twitter @markevans or MarkEvansTech.com. This post was originally published in February 14, 2012 on MarkEvansTech.com.
-
There are two types of startup incubators in the world: YCombinator or TechStars
Note: This is a guest post by Jesse Rodgers who is a cofounder of TribeHR. Jesse specializes in product design, web application development and emerging web technologies in higher education. He has been a key member of the Waterloo startup community hosting StartupCampWaterloo and other events to bring together and engage local entrepreneurs. Follow him on Twitter @jrodgers or WhoYouCallingAJesse.com.
Incubators and accelerators [Eds note: and cyclotrons] have but one purpose: move startups along in their life cycle at a faster pace than they would normally and increase the likelihood of a return by providing that service. If you are a startup looking at applying to an incubator you need to understand that the differences in how these programs differ go beyond the money they give you in exchange for equity.
An oversimplification of the incubator/accelerator space is to classify them as either a Y-Combinator (YC) or a TechStars (TS). If you really look at the booming world of incubators for high tech startups you see a model that either based on education and peers that is driven by a strong personality (YC) or a model that is more institutional, follows a script, and feels less personal but is more in line with how VC’s work (TS) (I would place 500 Startups right in the middle between YC & TS which is arguably representative of a third type). There is plenty to be found about the differences but here is a bit of a deeper exploration into the differences.
Startup lifecycle
Startups have a number of key phases in development that is best outlined in Fred Destin’s presentation on startup lifecycle.
- Start
- Launch
- Build
- Chasm
- Scale
With the 12-14 week cohort models, like YCombinator and TechStars, the focus should be on moving through starting and on to launch phase. There may be some that get into a build phase. The incubator or accelerator hopes that once they are done a 12-14 week program the startup will be in a much better position to move quickly through the build stage and at least take on the chasm phase.
Where I see the key difference between YC and TS is that YC seems to be able to get companies to go through stage 1 to 3 and they accept companies mainly in the start phase. TS seems to not attract a cluster of companies in a particular phase or not care about what phase a company is in.
The basics of an incubator/accelerator (whatever you want to call it)
Within the execution of any incubator or accelerator program there are, in my mind, 4 core stages in a typical cycle:
- Recruitment
- Onboarding
- In the program
- After the program
Within each of these of these stages there are a number of specific activities that all incubators do but in general they aren’t all that different.
Recruitment
YC currently leads the thought leadership with Hacker News, Paul Graham’s (PG) blog, and it’s success. Applicants fill out a form and once told they have an interview, travel to YC in Mountain View for an interview. They get just 15 min with a small panel and the panel does a bunch of tricks to the founders like carrying on side conversations – there are a lot of blog posts about that.
TechStars has adopted a more consistent process over it’s many affiliated programs (it appears) but they lack YC’s Hacker News or thought leadership (although they would claim otherwise). With Techstars there appears to be an affiliation with the Kauffman Foundation and the role they are taking in promoting the incubator model in general they have made themselves an authority in the space. From people I know that have been in the program it is a fairly standard process similar to raising Angel capital.
Onboarding
I am not sure on TS on-boarding but YC has a very short interview to decision to start of program window. YC has a little book that is like a long Wikipedia article written by Paul Graham that offers insights and baseline knowledge. From what I have been told the YC machine is pretty much immediately available to you when they say “you are in” — startups decide when to tell others. What is really interesting is that YC doesn’t announce it. They generally let a company know they are YC funded on the interview day but they don’t make a big announcement or anything.
Not having a big incubator announcement is a key difference here though. I will assume that with TS it is just like YC in that they have decided to fund you, they are now available to you. However, TechStars (it appears) doesn’t approach announcing the cohort in the same way as YC — they announce them ahead of the program.In the program: peer mentorship, startup culture
Each program runs for roughly 3 months, 12-14 weeks, where mentorship, various events, and a demo day to close it off normally occur. Each week is important given that each team only has 3 months. Over three months there are phases you can generally identify:
- Teams becoming familiar with each other, their mentors, and what they need to do (first 2 weeks).
- The heads down getting stuff done phase (8-10 weeks).
- Funding mode going into Demo Day (2 weeks).
Other incubator programs are fairly similar with any given week involving office hours (optional or required) and a speaker/dinner. The office hours are used to check in and place goals on the teams. Throughout the term there are demo nights, which are used by YC as a way to put peer pressure on other teams that might not be moving as fast as others.
Where they differ here is in the education of the founder(s). From everyone I have talked to that has gone through YC it seems to me it is a very challenging but rewarding relationship for a certain type of founder. That would make sense as a certain personality type will work best with Paul Graham’s way of doing things and will excel. I am not entirely sure it is simply a hacker/coder persona as most assume. I think it is a personality and learning style that goes a bit deeper.
TechStars has a co-working model with parts very similar to YC. The key difference is that TS doesn’t have the Paul Graham approach to educating founders so you will get very different details depending on who is running the program. TS also gives the startups a place to work where YC leaves them to find a house and work out of it.After the program: Alumni network
The key value any incubator or accelerator provides after the program is the alumni network of companies that are now a few steps ahead (depending on the age of the incubator there could be alumni with very large companies) of the current cohort in the program. Over time these alumni are your best mentors and connectors.
It is at this phase where the greatest value is for the startup, I believe. You now have access to what the old folks call a big rolodex (social graph) that will open many doors which essentially leaves it up to the entrepreneur whether their company will succeed or not. There are few to no barriers, generally speaking.
Any alumni of YC or Techstars still have contact with the folks in their cohort and all cohorts along with Hacker News. Techstars Network is so big they have a conference just for alumni while YC taps its alumni for all kinds of things. Also, founders seems to find going through the program a second time is different but just as valuable. These massive networks of successful alumni with a flock of high profile admirers is very similar to that of Higher Education alumni networks, so much so it convinces me that this entire process is a form of higher education.
Programs that work copy YCombinator, even TechStars did


 Some rights reserved by andi.vs.zf
Some rights reserved by andi.vs.zfThe current culture of education focused incubators started in my mind with YCombinator (started in 2005). I believe what we are seeing with the success of YC and TS is new take on graduate school. Both are different, both work, and people can have strong opinions either way. They feed a need that I don’t think people outside of incubators quite understand yet, learning to be a founder is really hard. Being a successful founder is even harder. The bet is that if you help young founders focus on what is important they will see success earlier or just simply see what success looks like.
If you are looking at an incubator anywhere (there are lots of great programs out there) you need to understand that the money is secondary. You need to find a program that will fit with the way you learn and has companies that you want to work with. It is just like how you picked your University or College except this time it can cost you a lot more (in equity) if you are successful.Note: This is a guest post by Jesse Rodgers who is a cofounder of TribeHR. Jesse specializes in product design, web application development and emerging web technologies in higher education. He has been a key member of the Waterloo startup community hosting StartupCampWaterloo and other events to bring together and engage local entrepreneurs. Follow him on Twitter @jrodgers or WhoYouCallingAJesse.com.
-
GrowConf Super Early Bird Pricing
The Grow Conference just released their first 50 “super early bird” tix at 50% off and sold out in less than a day! StartupNorth was able to secure 20 more “super early bird” tix for the StartupNorth audience to get that same price. Just register with the promo code – “startupnorth” and you’ll get the $295 price too (it says $395 – but you’ll get the discount).
Be sure to check out Debbie and Jason on their cross-country tour. I’ve heard that they’ll each be “manning” a kissing booth in Waterloo for their Valentine’s Day stop.
GrowConf is a great event that offers something for every entrepreneur.
-
Five-tool Players
I loved Moneyball (the movie). I also especially love sports analogies as they relate to technology and startups. While well-blogged about (Fred Wilson, Dave McClure, Dharmesh Shah), I believe these analogies are representative of what it takes to create and build a successful startup. While the premise of the book is to evaluate players based on data and metrics, I couldn’t help but tie back to the old school style of scouting in baseball to the current process we’re going through in selecting our cohort.
According to Wikipedia, in baseball, a five-tool player is one who excels at (1) hitting for average, (2) hitting for power, (3) baserunning skills and speed, (4) throwing ability, and (5) fielding abilities. I believe the same can be said for entrepreneurs.

Hitting for Average : Selling to Customers
In Moneyball, Billy Beane and his sidekick focus their team (the Oakland A’s) on one thing – getting on base – because getting on base equates to scoring runs, which equates to wins. In the startup world, scoring runs is the equivalent of getting cash, and this cash comes from customers.
Every entrepreneur needs to sell to customers. They need to generate revenue aka cash. It doesn’t matter if its enterprise customers, direct to consumer, professional services, white labeling, etc. Ultimately, if the startup is successful, they will sell to customers (which could also mean acquiring users). Effective hitters know where to hit the ball – pulling the ball, going opposite field, hitting gaps. Effective entrepreneurs know the gaps in the market amongst their competition and capitalize.
Hitting for Power : Selling to Investors
Chicks dig the longball. So how do you generate a huge amount of cash for your startup in one shot? You sell to investors. Entrepreneurs should also be able to successfully pitch VCs, angels, and other shareholders. This gives their companies cash in normally larger amounts than when selling to customers. It takes a special person to be able to raise from VCs. It takes a lot of time, energy, and follow-through.
A note on specialists here. In baseball, there are power hitters that specialize in hitting homeruns. Traditionally, these are the most popular and most sought after players because they have a halo effect around them. They fill seats, sell jerseys and advertising. They are the top billers and they usually can do no wrong (unless they cheat). In startups, this is also true because some franchises (VCs) want their own cleanup hitters at the top for the same halo effect.
Baserunning Skills & Speed : Hustle, Agility, and Speed
Running the bases in baseball is critical. If you can’t run the bases effectively, you’ll hinder your ability to score runs.
In startups, it’s critical to have that hustle and agility. This is all about opportunity maximization once the ball is in play. This means stretching a single into a double (crosssell / upsell, bigger contracts), stealing when possible (customers from your competition), and generally reading your competition in real-time (intuition and nuances of selling to both customers and investors).
Throwing Ability : Teamwork
This relates to the internal aspects of a startup. Can you lead and work within a team? Can you hit the cutoff man e.g. delegate when is the right time to do so?. This is about being affective with players on your own team to maximize the position you play. The most effective early stage startups I’ve come across have a good team rapport and play to each others’ strengths. Especially early when there is generally chaos, playing the position you’re best at (product, sales, marketing, customer services, QA, IT, etc.) and knowing your limits is critical.
Fielding Abilities : GTD
Every entrepreneur can get things done, and similarly every baseball player can catch a flyball or field a grounder. But the gold glove entrepreneurs are the ones that excel at cranking things out and simply getting things done across a broad range of domains. JFDI (thanks @msuster)! To borrow an American football analogy, this is the blocking and tackling that is the unglamorous and often overlooked aspect of entrepreneurialism.
Intangibles
There are definitely other things that make a successful baseball player and entrepreneur – experience, drive, fire, luck, durability, clutch ability, personal circumstances. Most things have to align for someone to be in the big leagues in baseball and technology.
Scouting
Over the last year as a VC, I’ve seen a lot of entrepreneurs with different combinations of these tools. Some were very effective at selling to customers, but just could not raise a round from VCs. Their pitches were too technical, they got into the weeds too much. They needed more sizzle. They were great at selling to customers, hitting their singles and doubles. But when it came to closing a round, they only had warning track power and process became that much more drawn out and painful.
On the flipside, there were companies where the only thing the CEO could do effectively was raise VC money. This left their companies with a lot of cash in the bank and a high valuation. Now they need to execute and build a product that would attract and acquire customers. Stay off the roids and start bunting if you need.
We are currently scouting players for our franchise. Are you a five-tool entrepreneur? If so, APPLY and come see us at Sprouter today. We’d love to help you develop into an MVP.
-
Founders & Funders An Update
I think Jevon and Jonas and Karthik are getting sick of running events with me. Before StartupEmpire back in 2008, I ended up in the Emergency Room at Toronto General for another look at my ticker. This week I ended up in the Emergency Room at Toronto General as we are planning Founders & Funders. I’m ok, I was both times but it does complicate the event planning and invitation process.
“Gentlemen, we can rebuild him. We have the technology. We have the capability to make the world’s first bionic man. Steve Austin will be that man. Better than he was before. Better…stronger…faster.” Wikipedia
So if you feel like you only got your invitation very recently, i.e., today. It’s my fault, I am sorry, I have been out of commission. It’s a reminder that you should do a startup before you need a body replacement.
Here is the update on Founders & Funders. It has been almost 2 years since we ran the last Founders & Funders (thanks for noticing William ;-). We are 7 days from the event and we have 35 remaining spots. Unlike past events, we are over inviting and over selling the event, i.e., first come first served. So if you got an invite but were waiting that might be a bad plan…
- 232 Invites sent
- 65 Tickets sold
- 35 Tickets remaining
- Target 70% Founders (Currently: 66% founders)
- Apply for Founders & Funders ?
How to get an invitation?
“Fortune favors the connected entrepreneur.” @jcal7 #trueuniversity via @hnshah
We’re looking for “interesting” founders. Often this means people that we’ve met at other events, as Founders & Funders are relatively small social gatherings. That doesn’t mean it is just our friends, as I’ve been often accused. But it is entrepreneurs that we’ve met, that are building interesting companies, that have interesting traction. Get someone that we think is awesome to refer you. It’s a social hack (just like me).
Connect with other founders

We have also decided to include a brief fireside chat with Daniel Debow at this dinner. We rarely do this sort of thing at a Founders and Funders but 2011 was such a great year we thought it would be fun to look back on the ups and downs of Rypple through the years and how they got to their eventual exit, some of which was written about in Forbes this week.
What’s the point?
Jonas, Jevon and I are founders. We are not an event company. We are not a media company. We have been trying to write content on StartupNorth that is relevant to us as founders. Whether we are raising money, connecting with other where we live, finding talent, or growing a business. We generally charge very close to the cost of the ticket, i.e., there are some slight over head costs but we are not collecting salaries or generating revenues. This is an unfortunate hobby. But I know there are world-class founders and companies across Canada and while there are government supported organizations and purported lobby groups, we are just a bunch of founders trying to do the things that we find useful in building our companies.
Founders & Funders is a social event. It is designed to connect with the people writing cheques and making investments on a social level. To talk about startups and technologies and business models without the constraints of a pitch. Will there be pitches, definitely (How do you know when an entrepreneur is dead? They stop pitching). The goal is to have a highly edited dinner party with “interesting founders” and get them out of their usual pitch oriented conversation with VCs.
Whether this works or not is questionable, but it does bring together founders and funders in a social context.
-
What’s Your Personality Type? Insights for Lean Entrepreneurs
Editor’s note: This is a cross post from Flow Ventures written by Raymond Luk (LinkedIn, @rayluk). Follow him on Twitter @rayluk. This post was originally published on February 1, 2012 on Flow Ventures.
 The ancient Greek aphorism “Know thyself” is very relevant to entrepreneurs. Most founders don’t give much thought to how their own personality type influences how well they run their startup. Remember, your reality distortion field distorts yourself too.
The ancient Greek aphorism “Know thyself” is very relevant to entrepreneurs. Most founders don’t give much thought to how their own personality type influences how well they run their startup. Remember, your reality distortion field distorts yourself too.The good news is that for the first time since I’ve been building companies, entrepreneurs share a common framework for guiding their startups: the Lean startup. Sure, some people don’t use the right vocabulary and misunderstand Lean. But I find that Lean thinking has permeated the entrepreneurial community, so much so that some founders are following the principles without knowing the term “lean startup” at all.
The bad news is that there’s still a huge gap between the understanding of lean startups and the practice. It’s frustrating to see and I think one reason is founders don’t take into account how their own personalities influence the process. I haven’t seen anyone ask: “How is my own personality getting in the way of being lean?”
To help answer that question, I’ve created a list of the top 5 personality archetypes I come across, as well as some things to watch out for if you recognize yourself in one (or more than one) of them:
- “Smartypants”– You’re very knowledgeable and you want people to know it. You love complexity. You believe that superior intellect and knowledge will close the sale, investment etc.
- Watch out: you’ll ignore the simple solution (which is often the best one) in favour of something more impressive. You’ll discount what customers say because they aren’t smart enough. You’ll be attracted to innovation vs execution.
- “Intelligent Architect”– Most engineers have this personality type. You like to build machines and you like it when they work as planned. You like the design phase of projects because there are no customers in the design phase…
- Watch out: you’re going to be very uncomfortable when your startup is trying to find a business model vs building a product. You can’t architect a solution when you don’t know what the problem is yet. Pivots will drive you crazy because there’s nothing wrong with the code.
- “The Advocate”– Most sales people (and almost all entrepreneurs) are strong when it comes to selling their vision or advocating what they believe in. In a meeting, especially a brainstorm, you talk rather than listen.
- Watch out: when you’re trying to find product-market fit, you’d better hone your shutting up skills. You can’t hear your customers’ voices when you’re still talking. You already know your own position, it’s time to listen to others.
- “The Dreamer”– I saw a pitch deck recently for a hyper-local startup. Great deck, nice screenshots, but within 5 minutes the entrepreneur admitted he probably would never use the product, nor did he think anyone else would. It’s easy to envision success IF everyone used your product. It’s harder to make it so.
- Watch out: you get excited about building an empire but you have a blind spot when it comes to actual customers and their problems. You’ll overestimate how well your product solves their problems.
- “Mom and Pop”– One great thing about Lean startups is that founders are getting in close proximity to customers to validate their businesses. Most people start with people they know in their community. If you’re a natural hustler, you’ve probably walked down Main Street knocking on doors and signing up beta customers.
- Watch out: You’ll hold as proof of your business the fact you signed up 10 restaurants in your neighbourhood. Instead of using (and possibly abusing) them to test your hypotheses, you’ll want to make them happy and get pulled in many directions. Be careful you don’t lose sight of the goal. You’re trying to build a scalable business, not a local consulting company.
Spend a bit of time thinking about who you are. Better yet, ask the people around you and make sure there are no sharp objects close by. There’s no value judgment here. There are no “good” or “bad” personality types. But the sooner you recognize your own personality type(s) the sooner you can get out of your own way.
nosce te ipsum
Editor’s note: This is a cross post from Flow Ventures written by Raymond Luk (LinkedIn, @rayluk). Follow him on Twitter @rayluk. This post was originally published on February 1, 2012 on Flow Ventures.
- “Smartypants”– You’re very knowledgeable and you want people to know it. You love complexity. You believe that superior intellect and knowledge will close the sale, investment etc.
-
Toronto: Why Are We Here?
Editor’s note: This is a cross post from Zak Homuth (LinkedIn, @zakhomuth, Github). Follow him on Twitter @zakhomuth. This post was originally published on February 1, 2012. And like many startups, Upverter is hiring.
Its winter right now, and that means for those of us in the north east its cold. We try to pretend its a good thing; that it keeps us focused. But the reality is we dont live and work here because of the snow, we live and work here because smart people love, more than anything else in the world [pg], to work with other smart people. And, make as many snow jokes as you want, but…
Pay attention to Toronto
Canada is the best country in the world to do business in [forbes], Toronto is the most multi-cultural city in the world [wikipedia] (suck-it NYC ;)), we get tax incentives for R&D [gov], and its the only city within an hour of one of the worlds foremost engineering schools [uwaterloo,coop program].
So, I say again, you should be paying attention. And if you’ve got your shit together you should be trying to figure out how to get a footprint here. Because believe it or not, we dont all want/have to be in the valley [fred].
All that being said, I still get this question a lot
There is a (very reasonable) expectation that YC companies make every effort to relocate to silicon valley as part of the program. And the fact that we have most of our operations in Toronto raises some eyebrows. My answer is really simple: The talent is here and it wants to be here. Sometimes I even go as far as talking about how much further our investment takes us when we spend it here instead of in the US, but at its root its a talent thing.
Toronto isn’t the only place in the world
Its true. I still spend a tremendous amount of time in the valley. And we have customers all over the world. Simply put there is no perfect place for everything. But if youre building a product business, or looking for talent, you could do much, much worse! Toronto is great for talent, and its a great place to live. Oh… and Im sure its not supposed to matter but like my good friend dave [blog] would say, “look at the scenery”.
But, its also a terrible place to raise money. Like I said, nowhere is perfect.
About Me
Upverter is my 3rd startup. I dropped out of highschool, and then university, both times to run startups. I’ve worked in Ottawa, Waterloo, Stuttgart, Bangalore, and Mountain View. I have never lived in Toronto before, so its a first for me, but we’re here because its where our team wanted to be. We are currently 7/7 kick-ass, and 6/7 Uwaterloo engineers who would just rather be here at home in Canada, than down in the valley. Oh, and if you’re smart, we’re hiring.
Editor’s note: This is a cross post from Zak Homuth (LinkedIn, @zakhomuth, Github). Follow him on Twitter @zakhomuth. This post was originally published on February 1, 2012. And like many startups, Upverter is hiring.